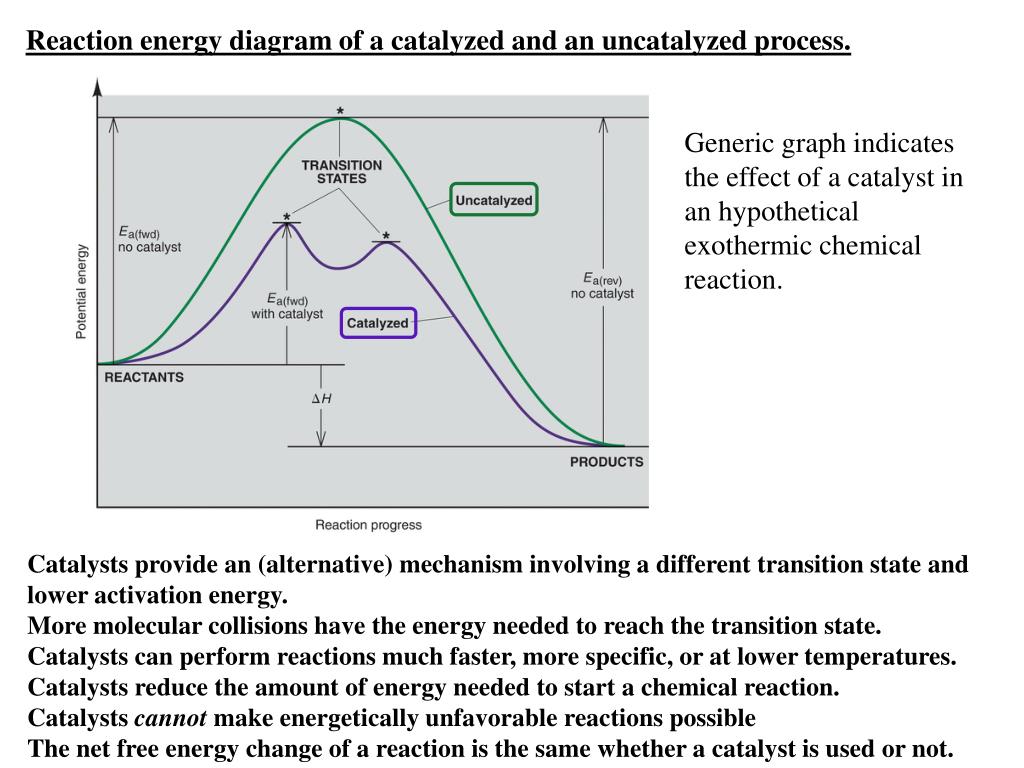
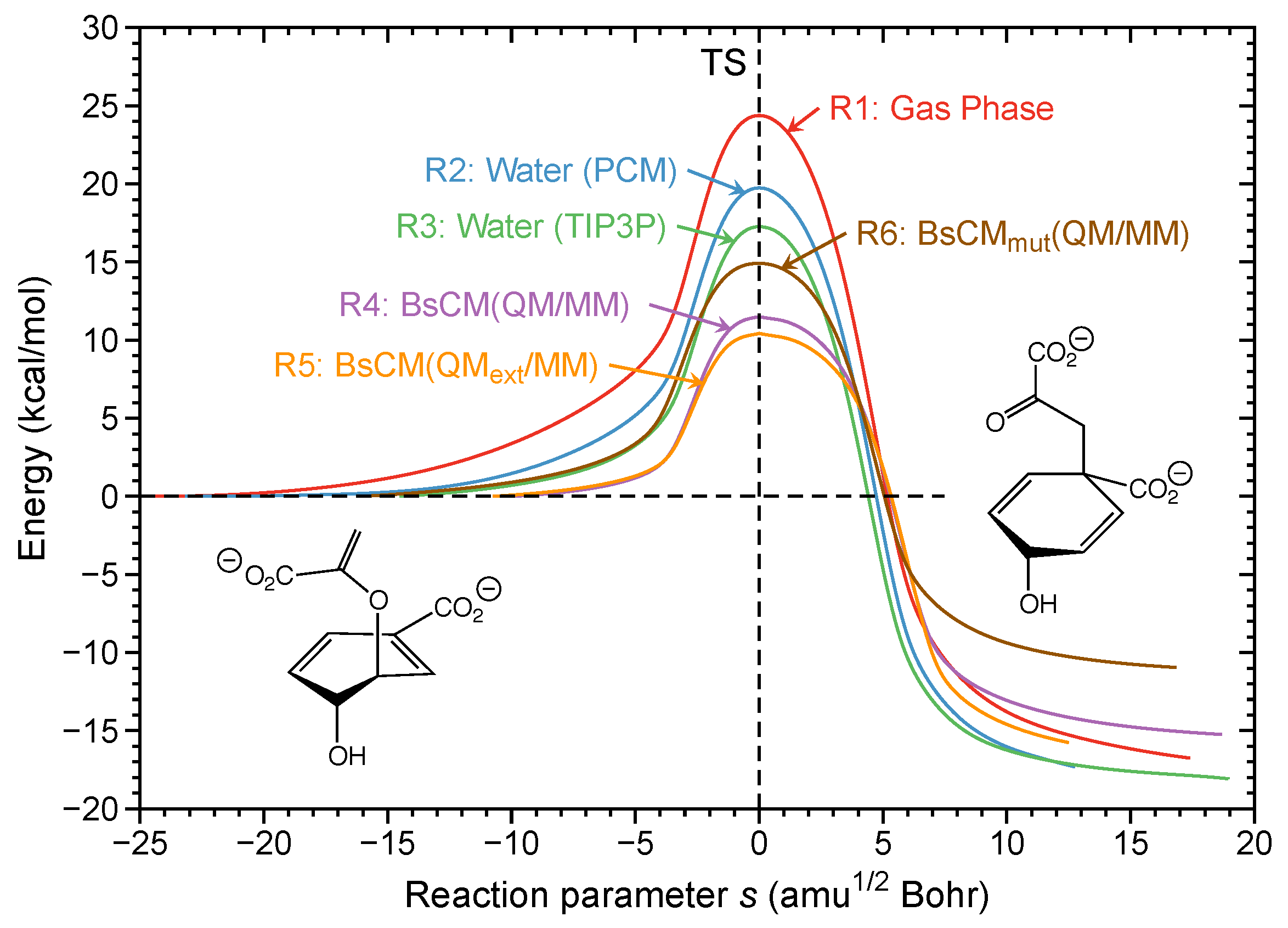
41 reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
Answered: (a) Draw an activation energy diagram… | bartleby (a) Draw an activation energy diagram for this reaction under catalyzed and uncatalyzed conditions and explain what it means for the activation energy to be lowered from 18 to 13 kcal/mol by ferric ions but from 18 to 7 kcal/mol by catalase. Please draw in the space provided below. Answered: Consider the following free energy… | bartleby Science Biology Q&A Library Consider the following free energy diagram for an uncatalyzed and enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Select all th statements that are true. Without enzyme With enzyme A+B Time AB O a. The rate of the enzyme catalyzed reaction is faster than the uncatalyzed reaction O b. The change in free energy for the reaction is greater ...
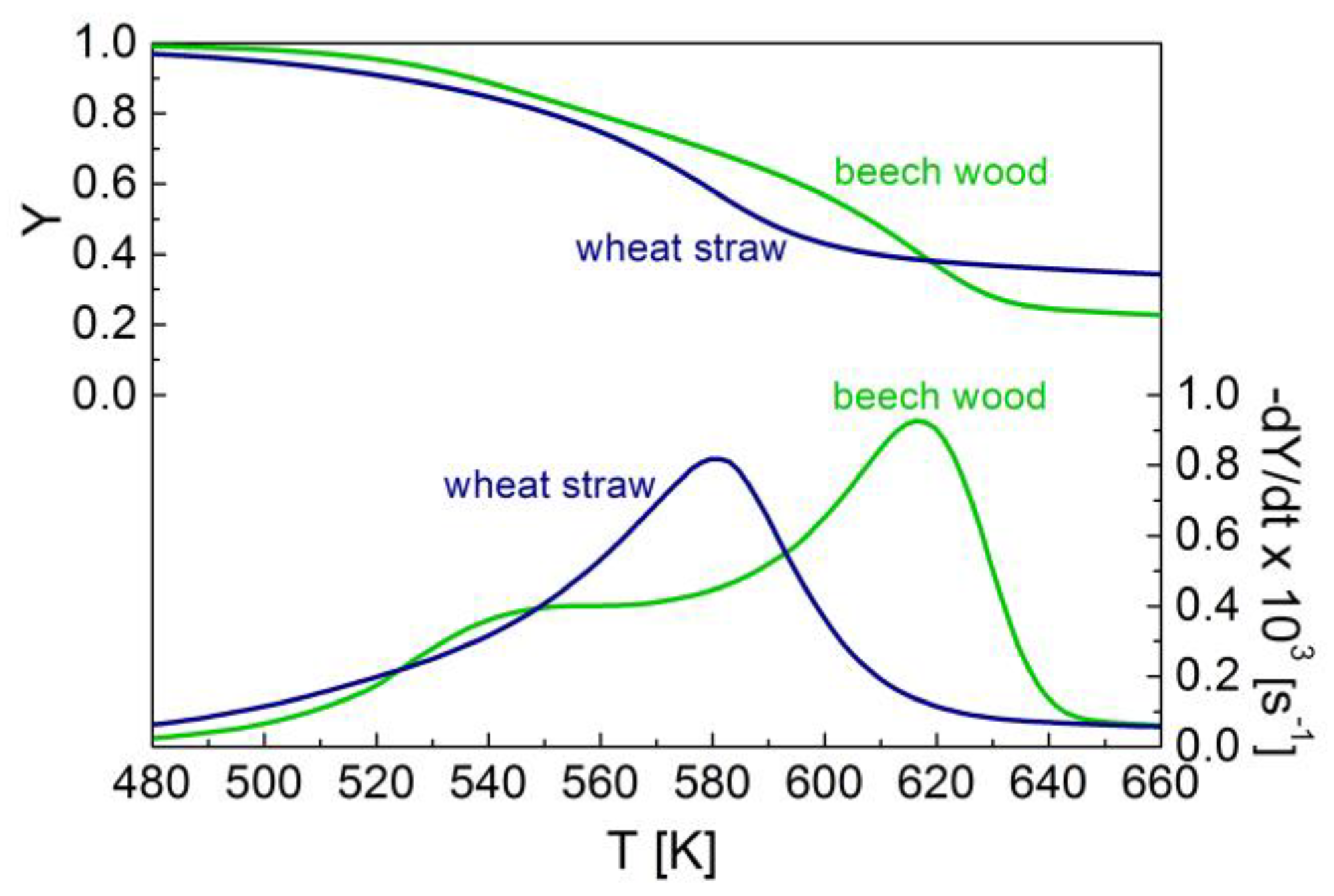
what is the difference between catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions The only difference between a catalyzed reaction and an uncatalyzed reaction is that the activation energy is different. An uncatalyzed reaction has a rate of 4.4 x 10-7 s-1 at room temperature (25 °C). Figure 1. the catalyzed reaction has a more favorable enthalpy change.

Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
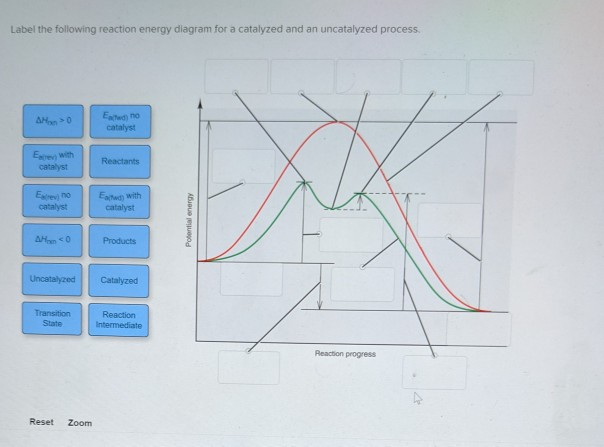
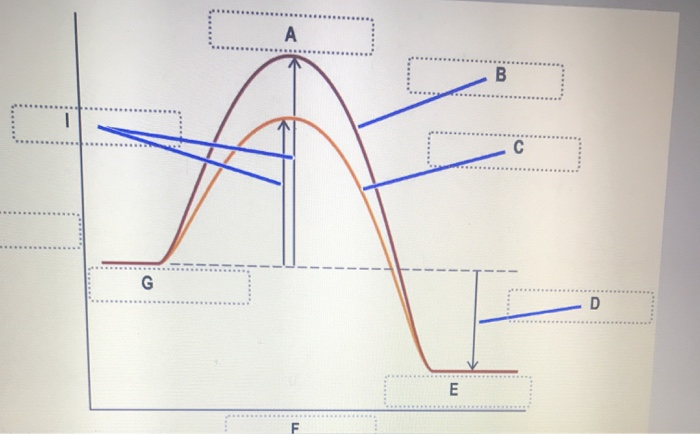
Catalysis - Chemistry One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in . Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd The enzyme itself is not used up in the process, and is free to catalyze the same reaction with a new set of substrates. Using various modifiers, the activity of the enzyme can be regulated, enabling control of the biochemistry of the cell as a whole. Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a - Chegg Best Answer. 88% (42 ratings) Transcribed image text: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process.
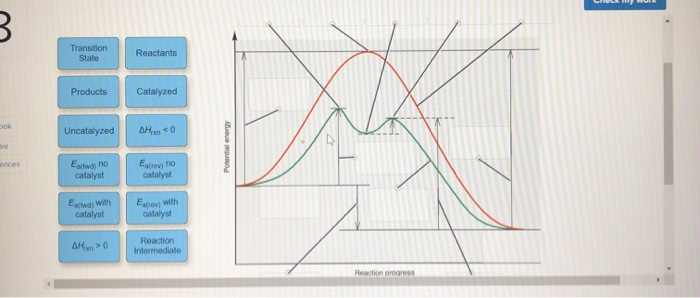
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a - Chegg Transcribed image text: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Transition State Transition State Transition intermediate Reaction Intermediate Transition State Transition Uncatalyzed Transition State Reactants Products Catalyzed Ea(fwd) no catalyst Uncatalyzed AHxn < 0 Potential energy Ea(rev) no catalyst Ea(fwd) no catalyst Ea(rev) no catalyst ... What is the difference between a catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction ... The only difference between a catalyzed reaction and an uncatalyzed reaction is that the activation energy is different. There is no effect on the. Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) Catalysis (12.7) - Chemistry 110 - Unizin Answer: For the first step, E a = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants. energy diagram catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reaction The energy diagram for a uncatalyzed reaction is an alternative way to describe a reaction. It's just a graph that shows the concentration of the reactant as well as the product. If your reaction isn't catalyzed, then the energy diagram will show this, meaning that the reaction has an exothermic reaction.
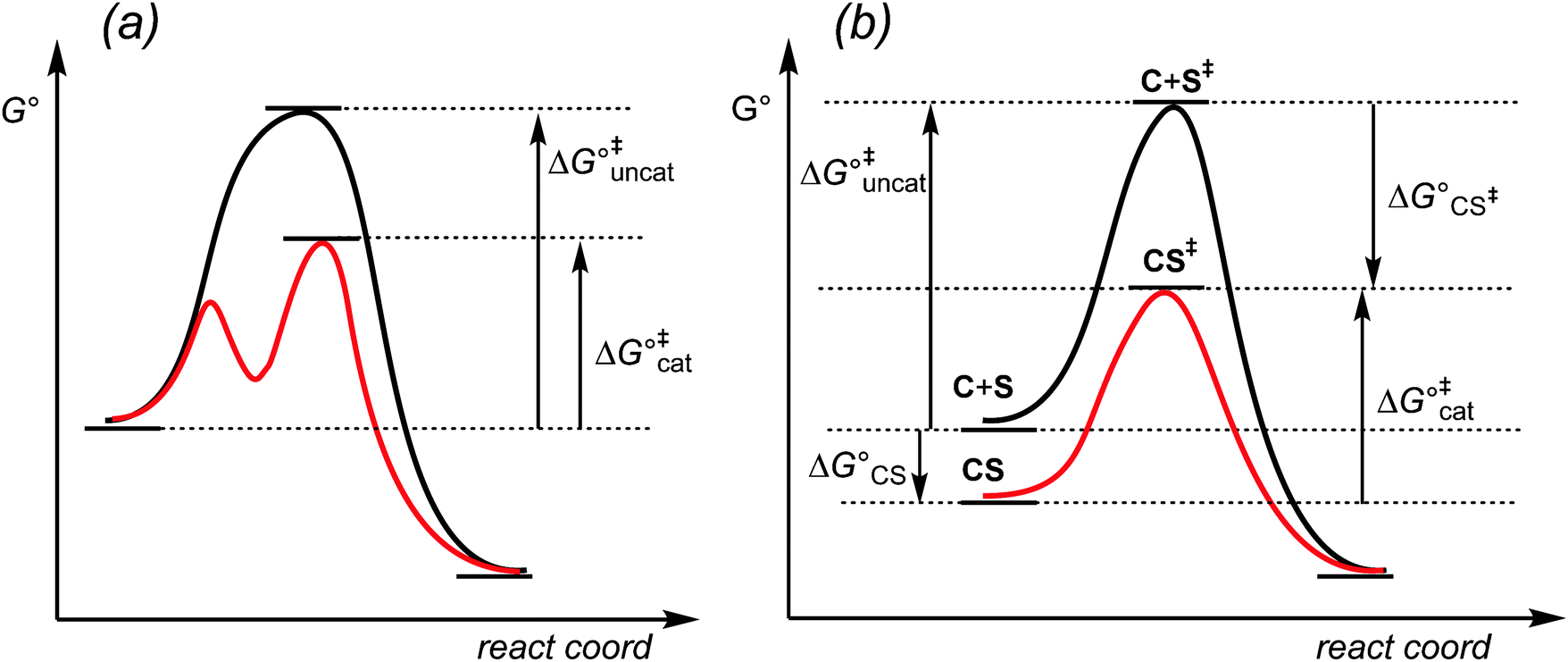
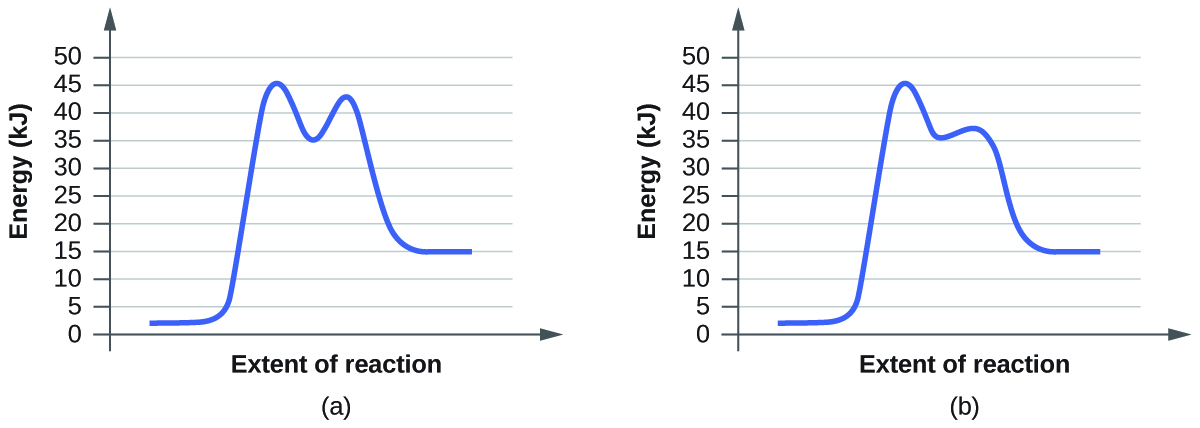
Diels–Alder reaction - Wikipedia The "prevailing opinion" is that most Diels–Alder reactions proceed through a concerted mechanism; the issue, however, has been thoroughly contested. Despite the fact that the vast majority of Diels–Alder reactions exhibit stereospecific, syn addition of the two components, a diradical intermediate has been postulated (and supported with computational evidence) on the grounds that the ... Reaction energy diagram of a catalyzed and an | Chegg.com Question: Reaction energy diagram of a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process Which statement about catalyst is true? Molecules cannot react with each other unless a catalyst is present. A catalyst decreases the activation energy of both the forward and the reverse reaction. A catalyst is consumed during a reaction. 38 The reaction profile diagram for the reaction sequence R X Y P is ... Consider the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions for the reduction of C 2 H 2 Catalyzed: C 2 H 2 (g) + H 2 (g) cat k C 2 H 6 (g) Uncatalyzed: C 2 H 2 (g) + H 2 (g) uncat k C 2 H 6 (g) uncat Which of the following statements about catalysts is incorrect. cat K K? A. The mechanism of the uncatalyzed reaction is different from the mechanism of the ... 4.6 Catalysis - Inorganic Chemistry for Chemical Engineers - BCcampus For the first step, Ea = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants.
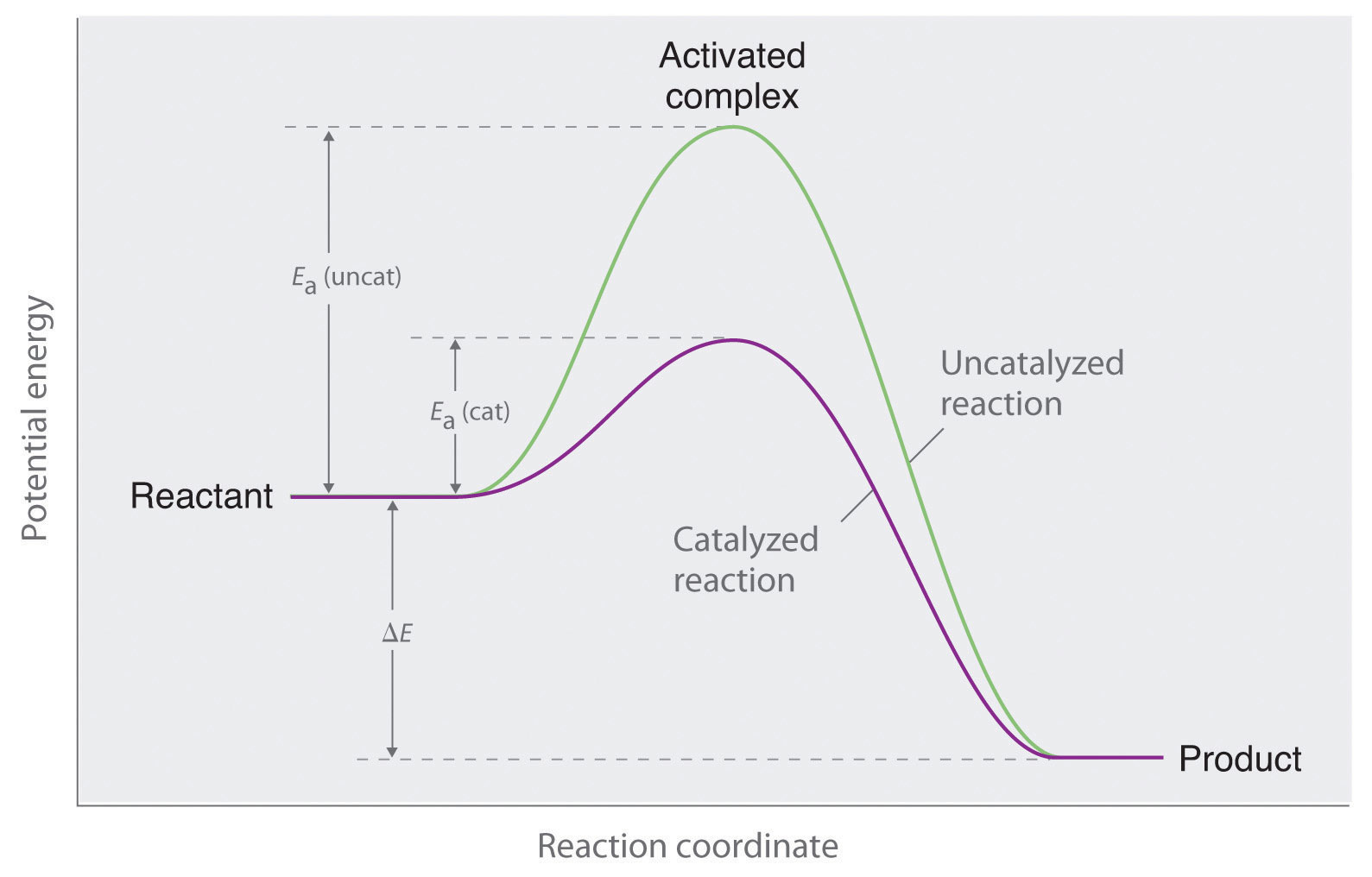
Answered: Sketch a qualitative reaction energy… | bartleby Sketch a qualitative reaction energy diagram for a chemical reaction with and without a catalyst. Assume the uncatalyzed reaction is endothermic. Note: Because the sketches are only qualitative, the energies in them don't have to be exact. They only have to have the right relationship to each other. SOLVED:Label the following reaction energy diagram for catalyzed and an ... VIDEO ANSWER:let's just ask this question. So here we need to label the following reaction energy diagram for the capitalized and unfertilized process. So let's draw this diagram. You know, we have this and here four C. This will be the levels open up McGee. So here we have an arrow, you will be in the middle, this will be the end over here and curie and So this would be the final 11 that we ... Energy Changes in Catalytic Reactions - QS Study A catalyst provides a different route with lower activation energy. Fig: Energy diagram for unanalyzed and catalyzed reactions. In Figure, the unanalyzed reaction is shown as a single step with high energy of activation. The catalyzed reaction is shown as a two-stage process with lower activation energy and is, therefore, faster. 12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 112- Chapters 12-17 of OpenStax ... - Unizin A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. This graph compares the reaction coordinates for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation.
Reaction Kinetics: Reaction Mechanisms - SparkNotes We will derive the Arrhenius Equation, which relates the rate constant for a reaction to its activation energy. Local minima on the reaction coordinate diagram are positions occupied by intermediates. By comparing the reaction coordinate diagram for a catalyzed and a uncatalyzed process, we can see that catalysts function by altering the route ...
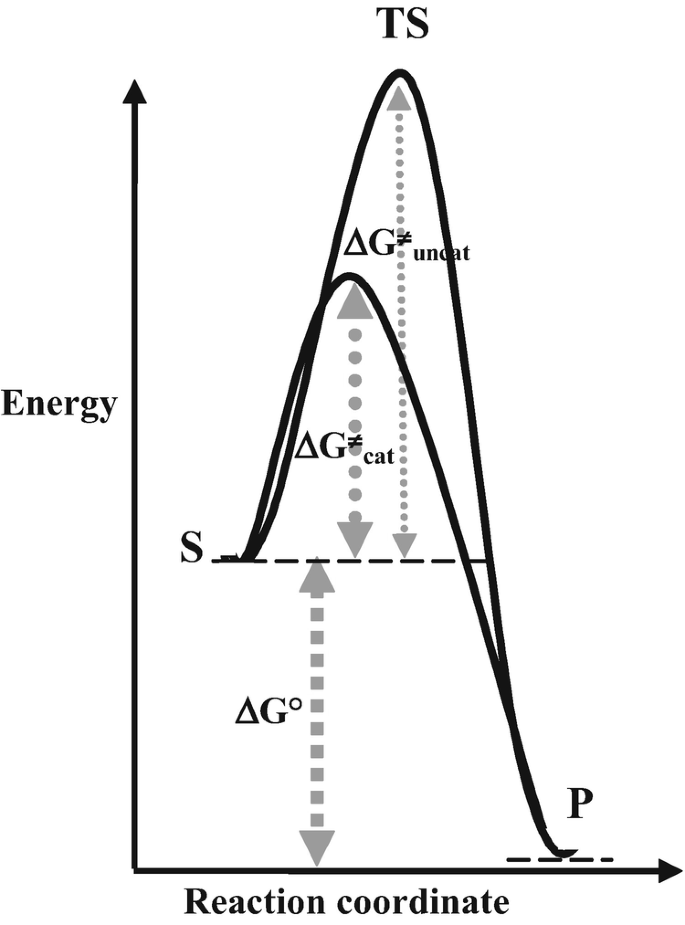
Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts and ... The energy diagram for a reaction model consisting of one enzyme, one substrate, and one product is depicted in many books where it is compared with that for the uncatalyzed reaction. The survey of several Biochemistry textbooks reveals a high diversity of profiles for the same process. A, C, and D are adapted from Refs. 5, 3, and 2, respectively.
Cold fusion - Wikipedia Cold fusion is a hypothesized type of nuclear reaction that would occur at, or near, room temperature.It would contrast starkly with the "hot" fusion that is known to take place naturally within stars and artificially in hydrogen bombs and prototype fusion reactors under immense pressure and at temperatures of millions of degrees, and be distinguished from muon-catalyzed fusion.
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax For the first step, Ea = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants.
18.7 Catalysis - Chemistry Fundamentals - University of Central Florida The two reaction diagrams here represent the same reaction: one without a catalyst and one with a catalyst. Estimate the activation energy for each process, and identify which one involves a catalyst. Show Solution. Activation energies are calculated by subtracting the reactant energy from the transition state energy. [latex]\text{diagram (a ...
enzyme catalyzed reaction diagram - thesolutionsunit.com Glycolysis is an almost universal central pathway of glucose catabolism. During glycolysis some of the free energy is released and conserved in the form of ATP and NADH. substrate. Example 1: Using Reaction Diagrams to Compare Catalyzed Reactions. It is not permanently used up; thus, it acts as a catalyst.
12.7 Catalysis | Chemistry - Lumen Learning One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1.
Answered: Label the components of an energy… | bartleby Answer Bank uncatalyzed reaction products activation energy reactants catalyzed reaction Reaction progress- Question Transcribed Image Text: Label the components of an energy diagram for a spontaneous reaction.
Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning The uncatalyzed reaction proceeds via a one-step mechanism (one transition state observed), whereas the catalyzed reaction follows a two-step mechanism (two transition states observed) with a notably lesser activation energy.
Catalysts Definition and How They Work - ThoughtCo A catalyst is not consumed by the reaction and it may participate in multiple reactions at a time. The only difference between a catalyzed reaction and an uncatalyzed reaction is that the activation energy is different. There is no effect on the energy of the reactants or the products. The ΔH for the reactions is the same. How Catalysts Work
What is the difference between a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed reaction ... What happen during catalyzed and uncatalyzed chemical reactions? Figure 1. The addition of a catalyst to a reaction lowers the activation energy, increasing the rate of the reaction. The activation energy of the uncatalyzed reaction is shown by Ea, while the catalyzed reaction is shown by Ea'.
Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a - Chegg Best Answer. 88% (42 ratings) Transcribed image text: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process.
Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry - Scribd The enzyme itself is not used up in the process, and is free to catalyze the same reaction with a new set of substrates. Using various modifiers, the activity of the enzyme can be regulated, enabling control of the biochemistry of the cell as a whole.
Catalysis - Chemistry One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in .





















Post a Comment for "41 reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process"