39 labeling a nucleotide
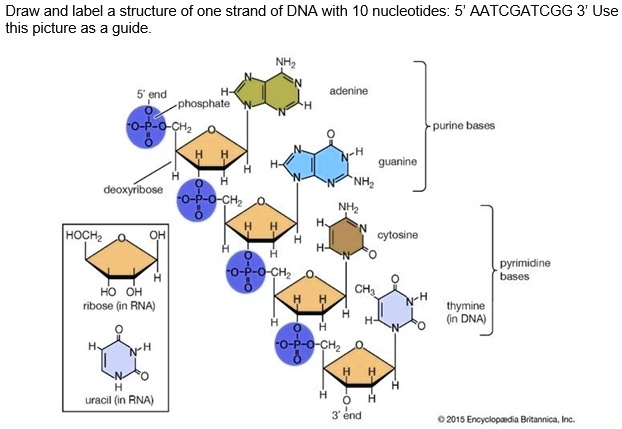
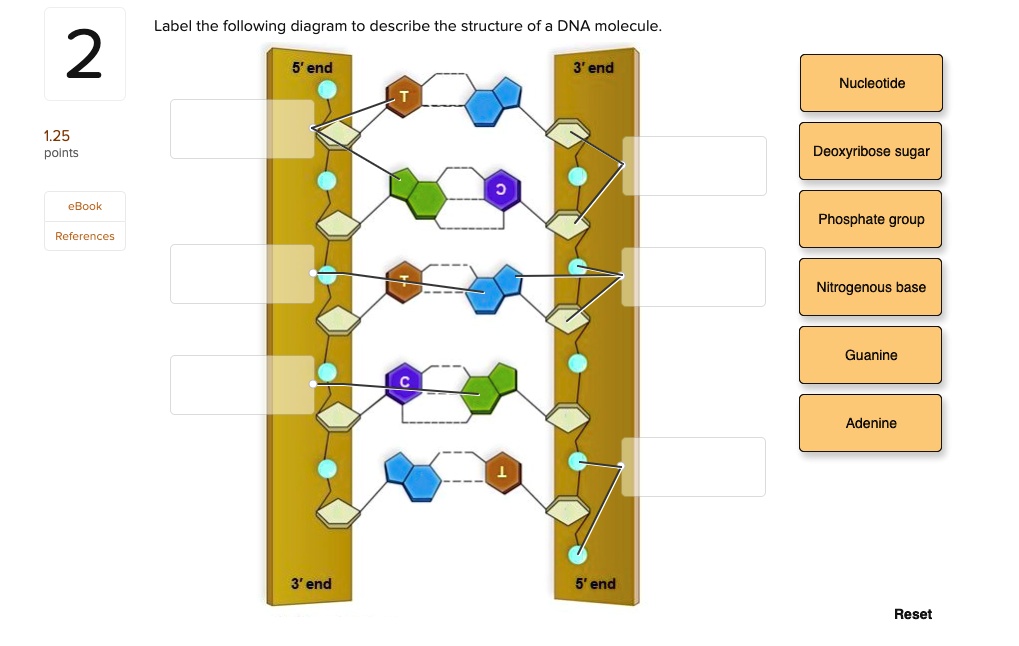
Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. - Brainly.com A nucleotide is a molecule composed of a pentose sugar (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. In DNA, there are four types of nucleotides that contain four different classes of nitrogen bases: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine. In RNA, Thymine bases are replaced by Uracil bases. 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Nucleotides are the building blocks of the DNA and RNA used as genetic material. Nucleotides also are used for cell signaling and to transport energy throughout cells. You may be asked to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded to each other. Here's the answer for both DNA and RNA.
Biotinylated Nucleotides for DNA Labeling - Jena Bioscience DNA Labeling cDNA Labeling; Nucleotide Cat. No. PCR NT Primer Extension 3' End Labeling RT; dUTP: Biotin-11-dUTP C5 position: NU-803-BIOX: 1,2: 2: 2: 2: 2: Biotin-16-dUTP C5 position: NU-803-BIO16: 1,2: 2: 2: 2: 2: dCTP: Biotin-11-dCTP C5 position: NU-809-BIOX: 1,2: 2: 2: 2: 2: Biotin-16-dCTP C5 position: NU-809-BIO16: 1: 2: 2: 2: 2: Biotin-14-dCTP N4 position
Labeling a nucleotide
dna-labeling | NEB Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or ... Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 the labeled aha-dutp and aha-dctp nucleotides can be used to generate labeled nucleic acid hybridization probes for many molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including two-color microarray assays, northern and southern blots, colony and plaque hybridizations, dna sequencing, primer extension, dna and rna amplification and … DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides - PerkinElmer Labeled nucleotides may be incorporated by a variety of methods including in vitro transcription with SP6, T3 or T7 RNA polymerase, 3' end labeling with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), T4 DNA polymerase or T7 DNA polymerase, random primed DNA labeling with Klenow fragment, cDNA labeling with AMV or M-MuLV reverse transcriptase, nick translation labeling with DNAse 1 and DNA Polymerase 1, and PCR labeling with thermophilic DNA polymerases like Taq or Pfu.
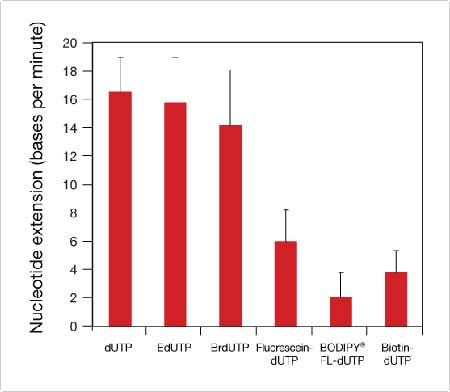
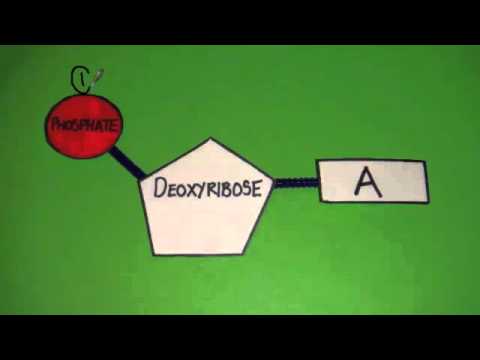
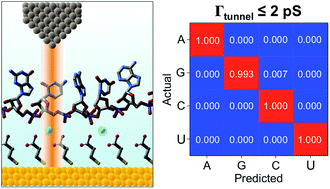
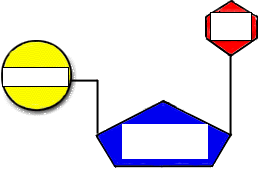
Labeling a nucleotide. How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group. 5-carbon sugar, and. nitrogenous base. Nucleotide - Wikipedia Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers - deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid, both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group consisting of one to three ... Nucleotide and Structural Label Identification in Single RNA ... - PubMed Here we present a method for direct nucleotide identification and structural label mapping of single RNA molecules via Quantum Molecular Sequencing (QMSeq). The method combines non-perturbative quantum tunneling spectroscopy to probe the molecular orbitals of ribonucleotides, new experimental biophysical parameters that fingerprint these molecular orbitals, and a machine learning classification algorithm to distinguish between the ribonucleotides. Incorporation of reporter-labeled nucleotides by DNA polymerases Most labeling protocols, such as nick translation and in vitro transcription use a modified nucleotide in combinations with the naturally occurring nucleotides ( 14, 17, 18 ). In many studies, it is highly desirable to synthesize probes with 100% of one or more of the nucleotide analogs at each position.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Radioactive_tracerRadioactive tracer - Wikipedia A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Fluorescence_in_situFluorescence in situ hybridization - Wikipedia In biology, a probe is a single strand of DNA or RNA that is complementary to a nucleotide sequence of interest. RNA probes can be designed for any gene or any sequence within a gene for visualization of mRNA , [3] [4] [5] lncRNA [6] [7] [8] and miRNA in tissues and cells. Fluorescent Nucleotides for RNA Labeling - Jena Bioscience cRNA Labeling by in vitro Transcription with... 3'-RNA Labeling by… Emission color Nucleotide Cat. No. T7 RNA Polymerase T3 RNA Polymerase SP6 RNA Polymerase yPAP thT T4 RNA Ligase; UTP: blue: UTP-PEG 5-AF405: NU-821-PEG5-AF405: 1: n/a: n/a: n/a: n/a-green: Fluorescein-12-UTP: NU-821-FAMX: 1: n/a: n/a: n/a: n/a-UTP-PEG 5-AF488: NU-821-PEG5-AF488: 1: n/a: n/a: n/a: n/a-UTP-ATTO-488: NU-821-488 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › 25559105ATAC-seq: A Method for Assaying Chromatin Accessibility ... Jan 05, 2015 · This unit describes Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-seq), a method for mapping chromatin accessibility genome-wide. This method probes DNA accessibility with hyperactive Tn5 transposase, which inserts sequencing adapters into accessible regions of chr …
dna-labeling | NEB DNA Labeling. Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end ... Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities. Draw And Label A Single Dna Nucleotide / Draw And Label Schematic ... Nucleic acids are made up of chains of many repeating units called nucleotides (see bottom left of figure 1 below). Draw a nucleotide and label the three main parts. Draw a nucleotide and label the three main parts. The above structure is a . The three parts of a nucleotide molecule are: Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends Nucleotides are chemical compounds that form the basic structure of nucleic acids like RNA and DNA. The chemical structure of nucleotides is almost the same regardless of whether or not the nucleotide is an RNA or DNA nucleotide. Nucleotides are made out of elements like nitrogen and carbon with a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar component, ...
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Summary of nucleic acid labeling methods. 1. 5′ end-labeled primers can be used with this method ...
› books › NBK209851FDA Regulatory Requirements for Nutrient Content Claims When a claim is made on a food that contains more than 13 g total fat, 4 g saturated fat, 60 mg cholesterol, or 480 mg sodium per RACC, per labeled serving, or, for foods with small RACC, per 50 g, a disclosure statement is required as part of claim (i.e., “See nutrition information for ___ content” with the blank filled in with nutrient(s) that exceed the prescribed levels).
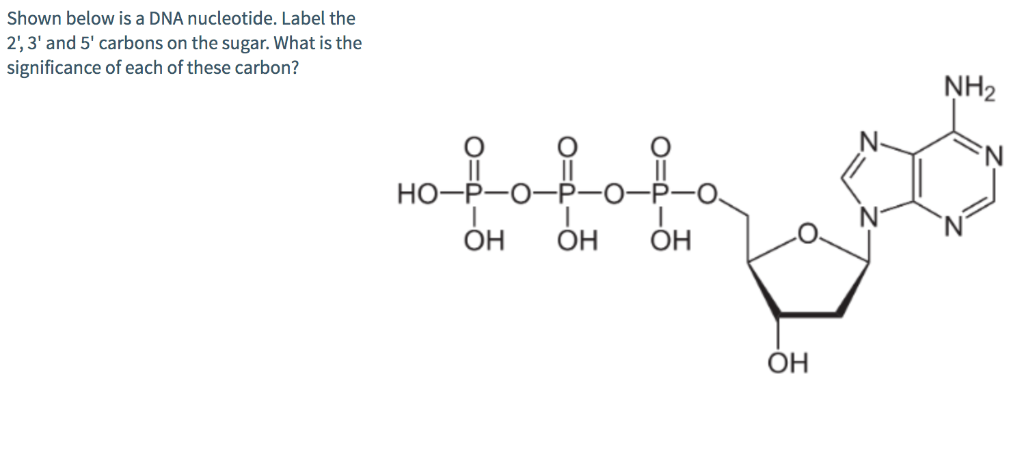
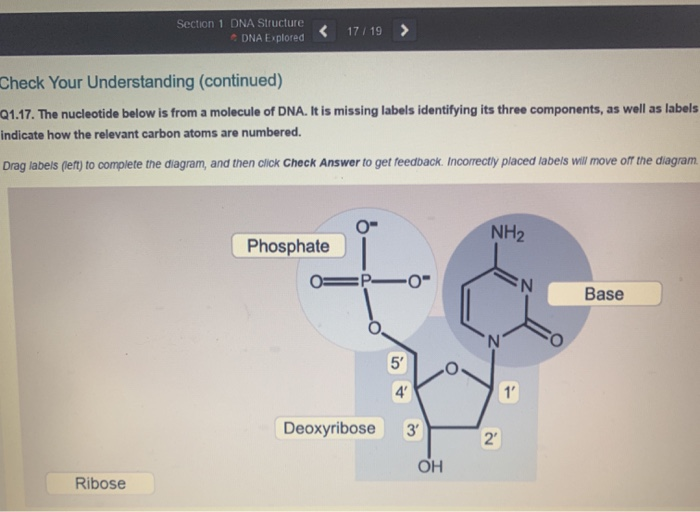
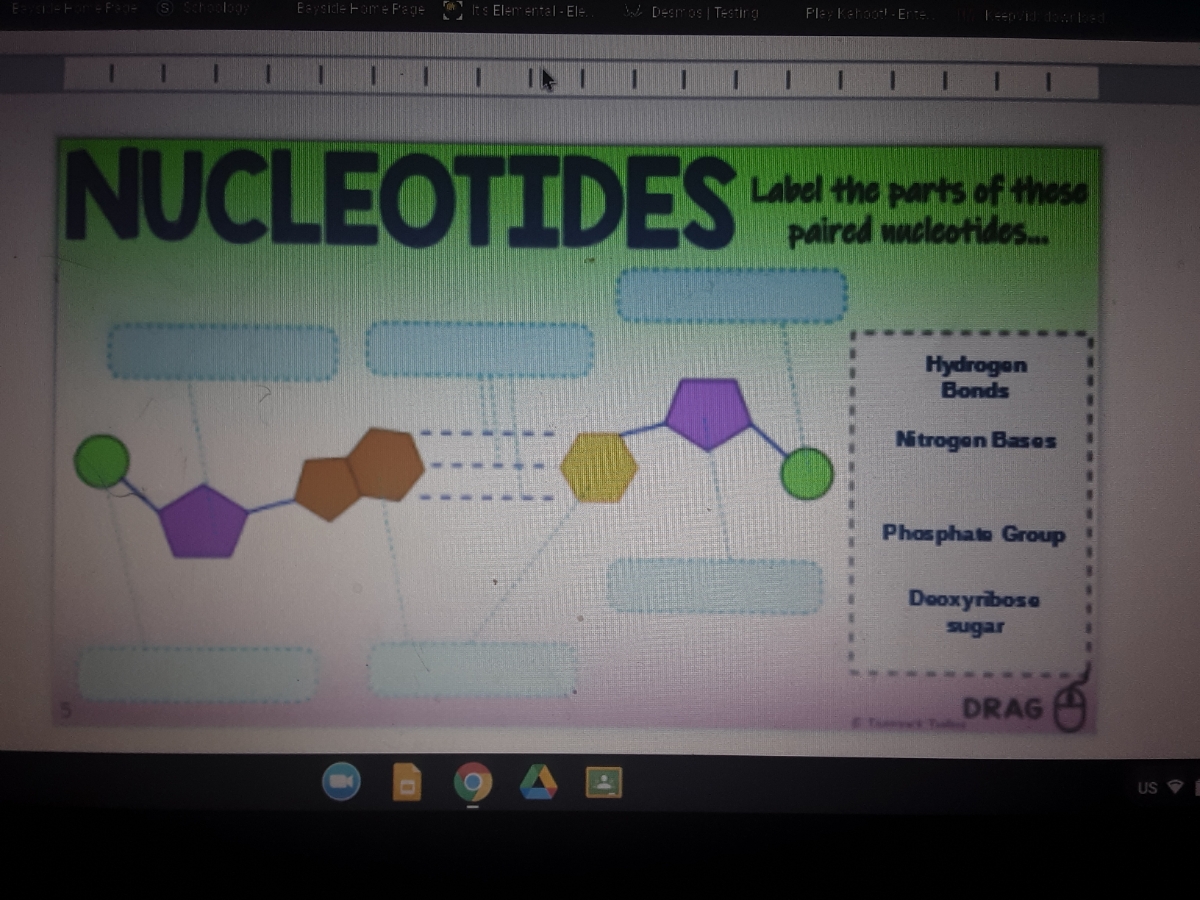
Nucleotides in DNA | Science Primer DNA is a nucleotide polymer, or polynucleotide. Each nucleotide contains three components: A five carbon sugar. A phosphate molecule. A nitrogen-containing base. The sugar carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5. The nitrogenous base attaches to base 1, and the phosphate group attaches to base 5. DNA polymers are strings of nucleotides.
programme.ueg.eu › week2022UEG 2022 - Programme 30 Years of UEG - Focus on Non-cardiac Chest Pain (NCCP): What has changed in the diagnosis and management?
dnasubway.cyverse.orgFast Track to Gene Annotation and Genome Analysis - DNA Subway DNA Subway Training. DNA Subway Training for Educators; DNA Barcoding and Metabarcoding for CURES Workshops; DNA Barcoding 101. Experimental method and everything else you need to generate DNA barcode sequences to analyze on the DNA Subway Blue Line.
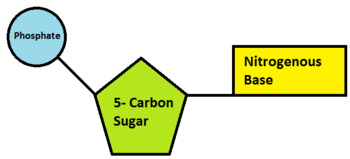
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine.
A nucleotide-independent cyclic nitroxide label for monitoring ... However, a general method for attaching a rigid label to nucleic acids in a nucleotide-independent manner has not been reported. Results: We developed an approach for installing a nearly rigid nitroxide spin label, designated as R5c, at a specific site of the nucleic acid backbone in a nucleotide-independent manner. The method uses a post ...
Digoxigenin (DIG) Labeling Methods - Sigma-Aldrich Digoxigenin (DIG) Labeling and Anti-DIG Antibody. The DIG System is the nonradioactive technology of choice to label and detect nucleic acids for multiple applications. The system is based on a steroid isolated from digitalis plants (Digitalis purpurea and Digitalis lanata). These plants are the only natural source of digoxigenin, so the anti ...
genepharma.com › enGenePharma Customer service +86-21-51320195. Address:Suite 602, 1011 Halley Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai 201203, P.R.China . Email:bd@genepharma.com
A nucleotide-independent cyclic nitroxide label for monitoring ... The results establish the applicability of R5c as a nucleotide-independent semi-rigid label for studying segmental motions in nucleic acids. Figure 1. A cyclic nitroxide label for nucleic acids. (A) A schematic of the labeling strategy. (B) Characterization of R5c labeling of the S c RNA by anion-exchange HPLC.
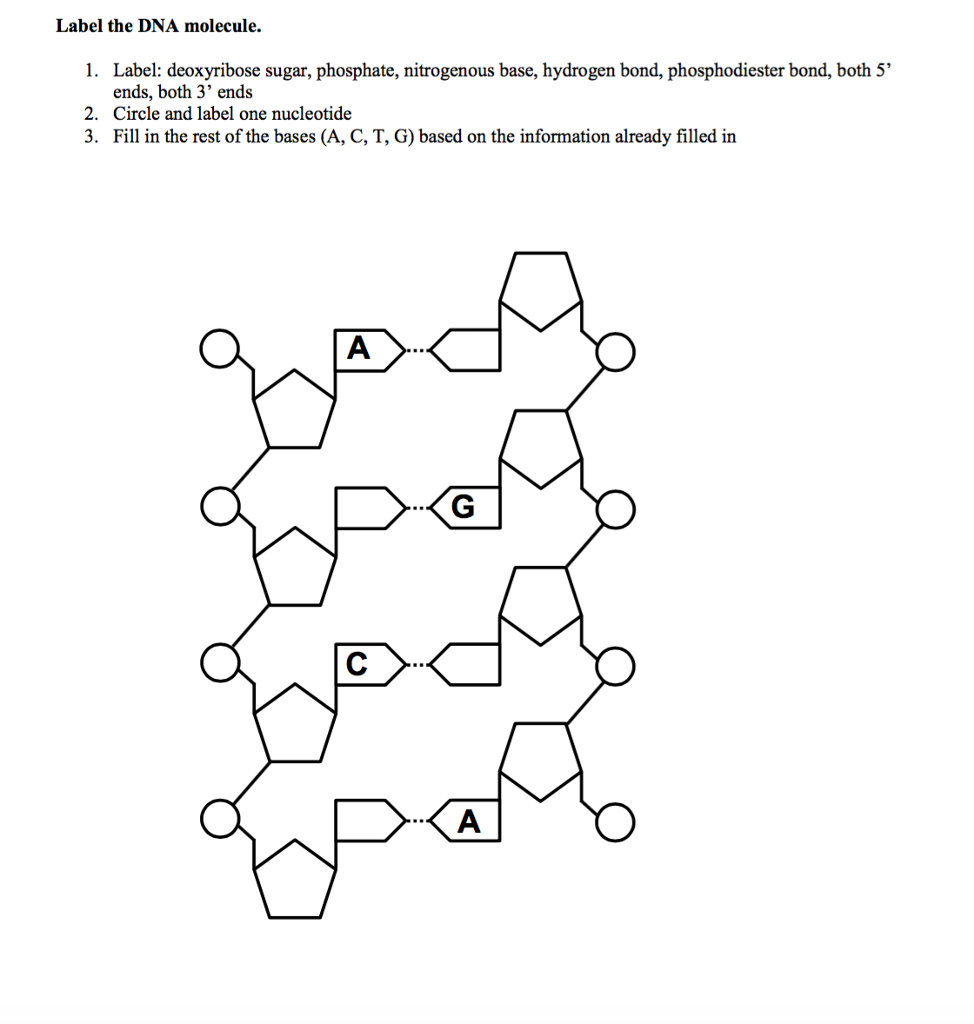
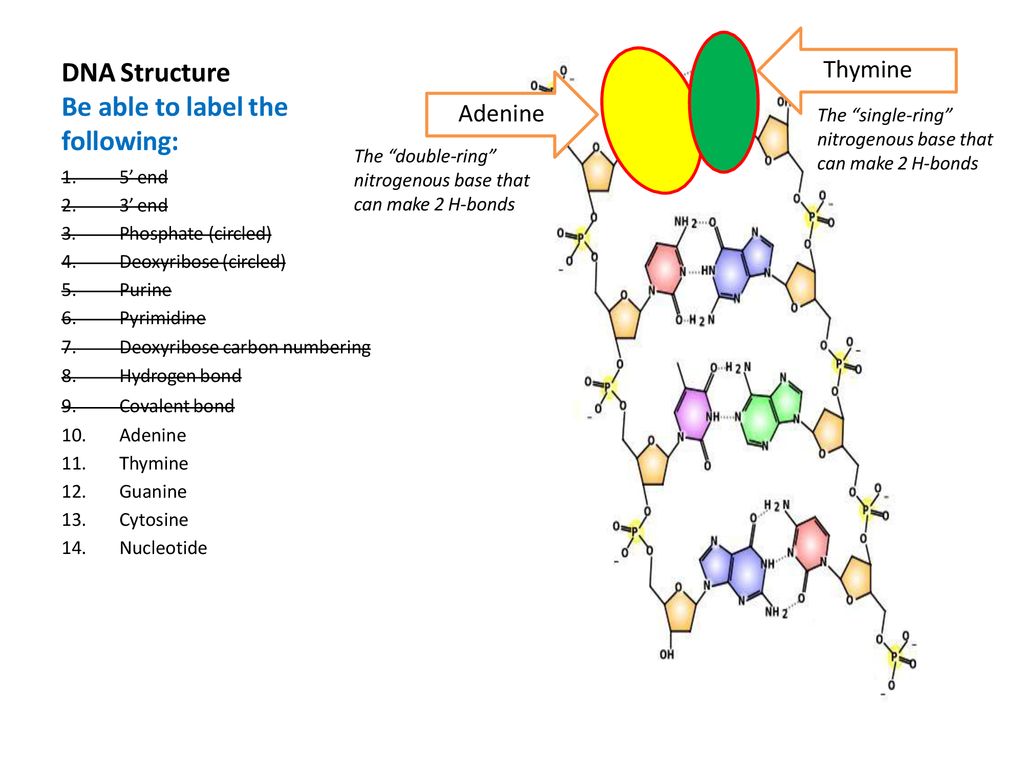
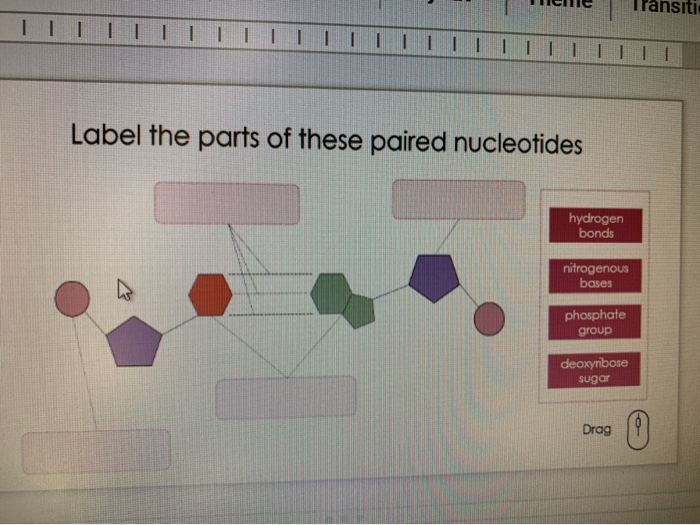
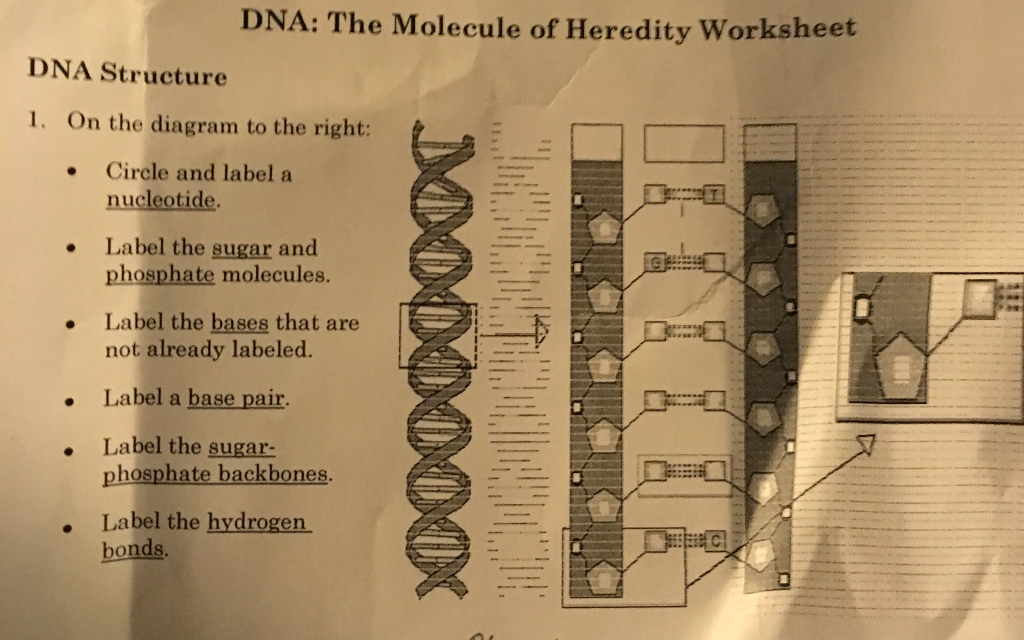
DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet Nucleotide. in a nucleic-acid chain, a sub-unit that consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base. Cytosine. The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA. Base Pair. A pair of complementary nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule. Hydrogen Bonds.
Labeled Nucleotides | Biocompare Labeled nucleotides can be incorporated into DNA or RNA fragments via methods such as nick translation, cDNA labeling and 3'-end labeling. Products (2522) User Reviews (2) Company View Product View Your search returned 2522 Labeled Nucleotides across 9 suppliers. Sponsored Products Alomone Labs, Ltd. α-Bungarotoxin-ATTO Fluor-633 Quantity:
Aminoallyl nucleotide - Wikipedia Aminoallyl nucleotide is a nucleotide with a modified base containing an allylamine.They are used in post-labeling of nucleic acids by fluorescence detection in microarray.They are reactive with N-Hydroxysuccinimide ester group which helps attach a fluorescent dye to the primary amino group on the nucleotide. These nucleotides are known as 5-(3-aminoallyl)-nucleotides since the aminoallyl ...
Nucleotide - Genome A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
The Structure of DNA - University of Arizona The Structure of DNA. Nucleic acids are made up of chains of many repeating units called nucleotides (see bottom left of Figure 1 below). The DNA molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix (spiral.) Nucleic acid molecules are incredibly complex, containing the code that guarantees ...
Nucleotide Numbering - Tulane University Nucleotide Numbering The nucleotides are shown with standard numbering convention. The aromatic base atoms are numbered 1 through 9 for purines and 1 through 6 for pyrimidines. The ribose sugar is numbered 1' through 5'. Atoms or groups attached to the base or sugar rings atoms have the same number as the ring atom to which they are bonded.
DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides - PerkinElmer Labeled nucleotides may be incorporated by a variety of methods including in vitro transcription with SP6, T3 or T7 RNA polymerase, 3' end labeling with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), T4 DNA polymerase or T7 DNA polymerase, random primed DNA labeling with Klenow fragment, cDNA labeling with AMV or M-MuLV reverse transcriptase, nick translation labeling with DNAse 1 and DNA Polymerase 1, and PCR labeling with thermophilic DNA polymerases like Taq or Pfu.
Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 the labeled aha-dutp and aha-dctp nucleotides can be used to generate labeled nucleic acid hybridization probes for many molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including two-color microarray assays, northern and southern blots, colony and plaque hybridizations, dna sequencing, primer extension, dna and rna amplification and …
dna-labeling | NEB Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or ...


















/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)


Post a Comment for "39 labeling a nucleotide"