41 correctly label the structures associated with unmyelinated nerve fibers in the pns.
(PDF) DiFiore's Atlas of Histology with Functional ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Peripheral Nervous System: Spinal Nerves and Plexuses - Antranik Each end of each plexus contains fibers from several spinal nerves. The fibers from each ventral ramus travels along different routes so that each limb muscle receives innervation from more than 1 spinal nerve to have a backup plan in case of injury. We have four plexuses: Cervical, Brachial, Lumbar, and Sacral.
16.4 The Peripheral Nervous System - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian ... The autonomic nervous system provides unconscious control over visceral functions and has two divisions: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is activated in stressful situations to prepare the animal for a "fight or flight" response. The parasympathetic nervous system is active during restful periods.
Correctly label the structures associated with unmyelinated nerve fibers in the pns.
12.1 Structure and Function of the Nervous System We can anatomically divide the nervous system into two major regions: the central nervous system (CNS) is the brain and spinal cord, the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the nerves ( Figure 12.1.1 ). The brain is contained within the cranial cavity of the skull, and the spinal cord is contained within the vertebral canal of the vertebral column. Anatomy, Central Nervous System - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf These regions are then broken down into 31 segments with 31 pairs of spinal nerves. There are 8 cervical nerves, 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves, 5 sacral nerves, and 1 coccygeal nerve. Each nerve exits the vertebral column passing through the intervertebral foramina and to its designated location in the body. Anatomy Midterm Lecture Flashcards - Quizlet Correctly label the structures associated with unmyelinated nerve fibers in the PNS. ... and the ability to secrete a chemical that will stimulate the next cell when an electrical signal reaches the end of a nerve fiber. ... Correctly label the structures associated with the lacrimal apparatus.
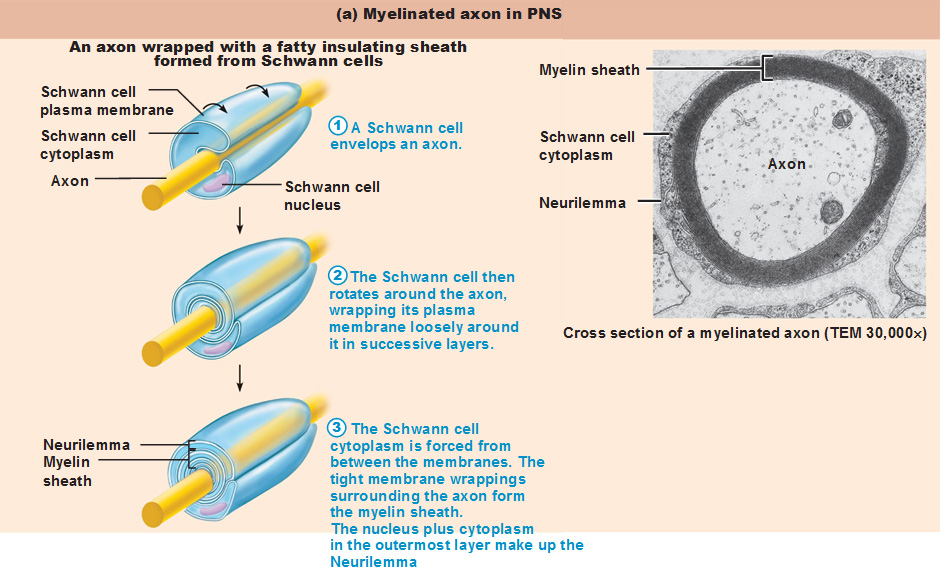
Correctly label the structures associated with unmyelinated nerve fibers in the pns.. Six Types of Neuroglia | Sciencing The peripheral nervous system, or PNS, is made up of the nerves in the rest of the body. In fact, along with neurons, they comprise the two types of cells in nervous tissue, and are integral to the functioning of the CNS and PNS. ... Glial cells do more than hold the brain together or provide structure, though. Scientific research is revealing ... The Peripheral Nervous System | SEER Training A connective tissue sheath called the epineurium surrounds each nerve. Each bundle of nerve fibers is called a fasciculus and is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Within the fasciculus, each individual nerve fiber, with its myelin and neurilemma, is surrounded by connective tissue called the endoneurium. visceral anatomy example - dublinwestsda.ie Correctly label the structures associated with unmyelinated nerve fibers in the PNS. Tears are more common in spots that are vulnerable. The word usage examples above have been gathered from various sources to reflect current and historial usage. Structure of the Autonomic Nervous System | Boundless Anatomy and ... A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion) is a nodule on a dorsal root of the spine that contains the cell bodies of nerve cells (neurons) that carry signals from the sensory organs towards the appropriate integration center. Nerves that carry signals towards the brain are known as afferent nerves.
Unit 4 Anatomy & Physiology Flashcards - Quizlet The Schwann cell's plasma membrane spirals repeatedly around the unmyelinated fiber as it does in a myelin sheath. false place the following in the order that an electrical impulse would travel beginning with the post-synaptic membrane 1. dendrite 2. soma 3. axon hillock 4. internode 5. node of rangier 6. terminal aborization 7. synaptic knobs 16.1 Neurons and Glial Cells - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition An axon is a tube-like structure that propagates the integrated signal to specialized endings called axon terminals. These terminals in turn synapse on other neurons, muscle, or target organs. Chemicals released at axon terminals allow signals to be communicated to these other cells. Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System - PMC Interestingly, 8% of the fibers that constitute a spinal nerve are sympathetic fibers. This allows for the distribution of sympathetic nerve fibers to the effectors of the skin including blood vessels and sweat glands. In fact, most innervated blood vessels in the entire body, primarily arterioles and veins, receive only sympathetic nerve fibers. Free Science Flashcards about ANP1040 Exam 4 - StudyStack Correctly label the structures, areas, and concentrations associated with a cell's electrical charge difference across its membrane. ... Spinal nerve, Perineum, Myelin, Epineuriun, Endoneurium, Myelinated nerve fiber, Unmyelinated nerve fiber: Which of the following structures is the richest in lipid content? -arachnoid mater -pia mater -white ...
Overview of neuron structure and function - Khan Academy Anatomy of a neuron. Neurons, like other cells, have a cell body (called the soma ). The nucleus of the neuron is found in the soma. Neurons need to produce a lot of proteins, and most neuronal proteins are synthesized in the soma as well. Various processes (appendages or protrusions) extend from the cell body. An Integrated View on Neuronal Subsets in the Peripheral Nervous System ... In the gastrointestinal tract, intrinsic neurons are those whose cell bodies lie within the organ, whereas extrinsic nerves (e.g. sensory nerve fibers) have their cell bodies outside the innervated organ. Typically, the soma of extrinsic sensory afferents is located within dorsal root ganglia, celiac ganglia, superior or inferior mesenteric ... Nervous System Questions and Answers | Study.com The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems comprise the: A. The central nervous system B. The peripheral nervous system C.The autonomic nervous system D. The somatosensory nervous system E... Which of the following are effectors a receptors b - Course Hero
Action potential - Definition, Steps, Phases | Kenhub An action potential is defined as a sudden, fast, transitory, and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential; that property is called the excitability. This article will discuss the definition, steps and phases of the action potential.
Post a Comment for "41 correctly label the structures associated with unmyelinated nerve fibers in the pns."